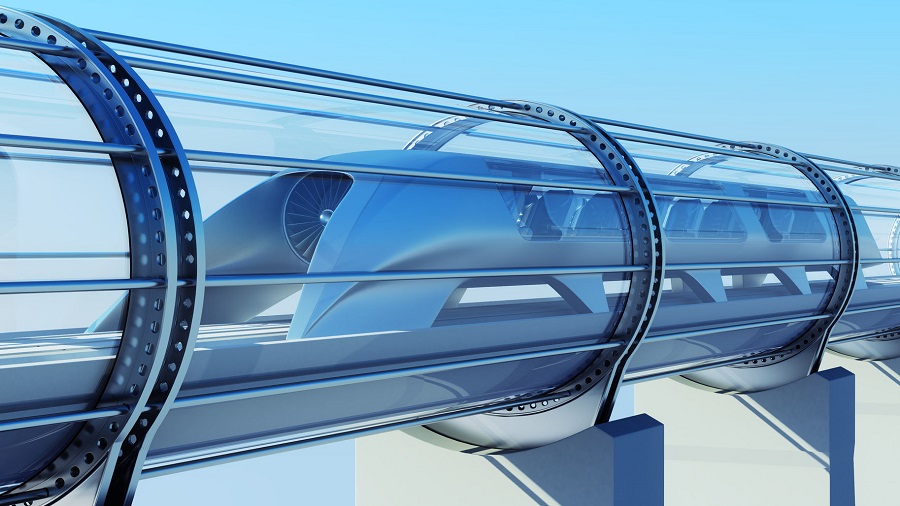
Countries seek to harness modern technological innovations to revolutionize their industrial sector and transportation services. One of these futuristic technologies is the Hyperloop, a high-speed transport system, which has been developed significantly during the recent period, using airless vacuum tubes with reduced air pressure.
The Hyperloop, or what is called "the Train of the Future", is expected to ferry people and goods at very high speeds, to provide a faster, safer and more efficient transportation. It is expected to lower the cost of shipping goods, provide excellent logistics services, and reduce the negative effects of conventional modes of transportation.
The Hyperloop Start
The Very High Speed Transit [VHST] System, which was launched in 1972, was the precursor of the Hyperloop. The idea was further developed by Elon Musk, a renowned businessman and the owner of the PayPal payment system and two other companies, Tesla and SpaceX, to whom the Hyperloop technology is attributed. Musk described his idea in March 2013 as the fifth mode of transportation for passengers and goods (after the four modes: planes, trains, cars and boats). The core idea of the Hyperloop is based on using air pods that travel in hard aluminum -frame and airless vacuum tubes with reduced air pressure. It travels at the speed of 1200 km per hour. It is powered by solar panels, and for more propulsion, magnetic accelerators will be planted along the length of the tube.
The first test was carried on May 11, 2016, in Nevada desert, US, where the capsule was launched at the speed of 100 miles per hour.
Hyperloop Advantages
Hyperloop technology provides a range of advantages that make it an ideal means of transport between cities, especially in light of the challenges facing the transportation sector in terms of cost, safety and lack of sustainability. Hyperloop advantages includes the following:
1- Speed: Hyperloop technology provides high speed, up to 1200 km/hour, exceeding the speed of any existing means of transport, even the planes that can fly at 800 km/hour.
2- Safety: It provides high safety measures through the electric operating systems, electric brakes and airbags.
3- On-demand response: the time intervals between Hyperloop capsules are very short, as it can launch a capsule to passengers at an average rate of 10-30 seconds per line without risk of collision or derailment.
4- Immunity to weather conditions: capsules are launched inside closed tubes, eliminating any delays or any costly repercussions that may be caused by weather conditions.
5- Environmental friendly technology: the Hyperloop is contamination-free, carbon emissions-free, and powered by solar energy.
6- Driverless: there is no need to hire a driver for the capsules, eliminating the human errors of driving.
7- Low cost: estimates indicate that the cost of building a single tube equals 10 per cent of the cost of building a high-speed traditional train.
8- More convenient to transport passengers and goods: passenger capsules have comfortable and well adapted seats. In addition, other capsules are equipped to transport goods without causing any damage.
Implications on Industrial and Transportation Sectors
The Hyperloop offers a number of competitive advantages regarding the transportation of goods and passengers, which are expected to have a positive impact on the industrial sector in general and transportation in particular, as follows:
1- Revolutionizes the industrial sector: This sector is facing many challenges relating to transportation services, because the existing solutions are unsustainable. The Hyperloop offers highly efficient and sustainable solutions to solve such problems. It is expected to acquire a large volume of industries that amounts to trillions of dollars.
2- Reshapes shipping and logistics industries: In relation to transporting goods, the Hyperloop capsule can carry one or two containers with a load equivalent to 40 feet without any delays. A capsule can be launched within short time intervals, allowing a major leap in the world of shipping and logistics, which makes the Hyperloop a fast and cost-effective means of cargo shipping.
3- Reduces economic losses and provides welfare for individuals: The Hyperloop provides solutions to traffic jams, and transportation in all weather conditions. Such advantages are not available in other means of transport, which entail many economic losses.
4- Supports building of offshore docks & dry ports: The Hyperloop provides the opportunity to build independent seaport, to be located 30 km from the shore, and connect it to the coasts through a network of tunnels to create new distribution centers. Moreover, loading and unloading containers a mile from coastline, without approaching the vessels, allows for the reutilization of the waterfront. Overall, this technology maximizes the capacity and efficiency of ports, as well as integrating technological developments in logistics.
5- Helps the shift towards smart cities: The Hyperloop capsules are designed to have stringent measures with regard to security and safety, as well as environmental control and life support system (ECLSS). This new technology can connect the major cities in the world, providing shorter-time and cheaper trips.
6- Offers the opportunity to move across land and sea: The Hyperloop can be used on land and in the sea. On land, it does not require paved roads, as it can travel easily through natural barriers, due to the capsules’ low mass and tube’s resistance to external pressure. In the sea, it does not require much space. It is designed to enable external seaports with a delivery mechanism of goods to internal ports through small tunnels.
7- Contributes to the growth of the On-Demand Economy: One of the advantages the Hyperloop offers is providing an on-demand service. Citizens do not need to wait for a long period as one capsule fits 28 or more passengers, and is launched every 10-30 seconds interval per line without any risk.
This enhances safety, particularly given that more than 1.2 million people are killed and about 50 million are injured annually because of road accidents in the world. Low and middle-income countries constitute 90 percent of these deaths even though they own half of the cars in the world.
8- Reduces energy consumption and pollution: the Hyperloop provides a model of efficiency and reduction of energy consumption because it depends on solar energy. Thus, it helps address the challenges of the global transportation sector, which constitutes about 60 percent of the global oil consumption, 27 percent of total energy consumption, and 23 percent of carbon dioxide emissions related to energy in the world, according to the World Bank data.
9- Creates job opportunities: In light of the expected positive effects of the Hyperloop technology on the industrial sector, it will assist in creating new job opportunities. It is estimated that an average of 200 million jobs will be available for youth in the Middle East and North Africa, according to Nick Earle, Senior Vice President for global operations at Hyperloop One, in a speech at the Global Manufacturing and Industrialization Summit held in Abu Dhabi in March 2017.
UAE interest
In the Middle East region, the UAE has taken the lead in adopting the Hyperloop technology and exploring its application within the coming years, to deliver high quality and innovative services worthy of its leading position in the region that aspires to provide futuristic solutions in all sectors. The Hyperloop system is expected to be built in the UAE over the next five years, according to remarks in last November by Rob Lloyd, the Chief Executive Officer of Hyperloop One.
In this context, the Office of His Highness Sheikh Falah bin Zayed Al Nahyan, signed a strategic partnership agreement with Hyperloop One in January 2017, to transfer this technology to Abu Dhabi. This comes as part of the efforts to support the strategic project of linking the cities of Abu Dhabi and Al Ain using the hyperloop techniques. This agreement comes in line with Abu Dhabi Vision 2030 and its focus on developing leading infrastructure in the region and the world.
Earlier, the Roads and Transport Authority (RTA) in Dubai announced in November 2016, that it had signed an agreement with Hyperloop One, to launch a revolutionary high-speed transport project. This comes in alignment with Dubai strategy for self-driving smart transportation, which aims at transforming 25 per cent of total trips in Dubai into smart and self-driving ones. The move came after Hyperloop One signed Memorandum of Understanding with Dubai World Ports last August to transport containers via the Hyperloop system from vessels at Jebel Ali Port to container depot in Dubai.
Hyperloop One plans to tap investments in other Gulf countries, especially that the Hyperloop train will help people travel between Gulf cities within an hour or less, which will in turn make a huge leap in various economic sectors. The company also plans to inject about USD 7 billion of investments in the air cargo sector in the Gulf, USD 3 billion in road and rail freight, and USD 2 billion in maritime shipping.
Overall, the high-speed Hyperloop technology is expected to make an enormous surge in the transport industry worldwide, prompting several states to consider implementing this technology because of the great advantages it offers: the high-level of safety, shorter time to transport passengers and cargo, and to complete business transactions, increasing productivity, and reducing environmental pollution, among other things.